Glossary
Definitions
ANBERD: Analytical Business Enterprise Research and Development (OECD database).
Applied research: Original investigation undertaken to acquire new knowledge. It is directed primarily toward a specific practical aim or objective. See OECD (2015).
Basic research: Experimental or theoretical work undertaken primarily to acquire new knowledge of the underlying foundations of phenomena and observable facts, without any particular application or use in view. See OECD (2015).
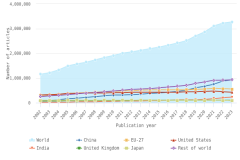
Citations: Citations document prior research relied on for science and engineering (S&E) publications. Thus, citations provide an indication of the flow and possible impact of new knowledge within and across scientific fields, sectors or institutions, and geographic locations.
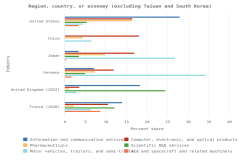
Coauthorship: When more than one author is listed on a publication. An article is considered to contain an international coauthorship when institutional addresses for its authors are located in two or more different regions, countries, or economies. Publication counts of coauthorship use whole counting, so each location contributing to the article receives credit for that article. This indicator can be used to measure collaboration across geographies.
European Union (EU-27): The EU comprises 27 member nations: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, and Sweden. The United Kingdom withdrew from the EU on 1 February 2020. Unless otherwise noted, EU data include all current 27 member countries.
Experimental development: Systematic work, drawing on knowledge gained from research and practical experience and producing additional knowledge, which is directed to producing new products or processes or to improving existing products or processes. See OECD (2015).
Fractional counting: A method of counting S&E publications in which credit for coauthored publications is divided among the collaborating institutions or regions, countries, or economies based on the proportion of their participating authors. Fractional counting allocates the publication count based on the proportion of the coauthors named on the article with institutional addresses from each region, country, or economy. Fractional counting enables the counts to sum up to the number of total articles.
Gross domestic product (GDP): The market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period.
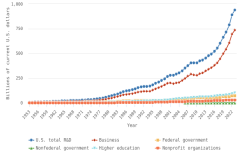
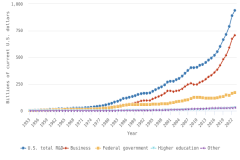
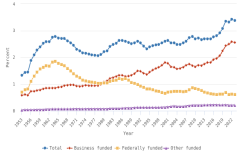
Gross domestic expenditures on R&D (GERD): Defined by OECD as the total expenditure (current and capital) on R&D carried out by all resident companies, research institutes, and university and government laboratories in a country. It includes R&D funded from abroad but excludes domestic funds for R&D performed outside the domestic economy (https://data.oecd.org/rd/gross-domestic-spending-on-r-d.htm).
Highly cited article (HCA): An HCA ratio provides an indication of scientific impact (Waltman, van Eck, and Wouters 2013). The HCA ratio for a country or other geographic location is calculated as the share of all articles published in a given year by authors with institutional addresses within that location that fall within the top 1% by citation count of all articles published that year, measured for each research field. The HCA ratio is indexed to 1.00, so a location whose authors produce highly cited articles at the expected (i.e., global average) rate has an HCA ratio of 1.00—that is, 1% of the location’s articles are among the top 1% of the world’s highly cited articles. A location with an HCA ratio greater than 1.00 is producing a disproportionately high level of articles with exceptional scientific impact, whereas a location whose authors produce relatively fewer influential articles will have an HCA ratio below 1.00.
Main Science and Technology Indicators (MSTI): An OECD database.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD): An international organization of 38 countries, headquartered in Paris, France (https://www.oecd.org/en/about.html). Among its many activities, OECD compiles social, economic, and science and technology statistics for all member and selected nonmember countries.
Purchasing power parity (PPP): Currency conversion rates that try to equalize the purchasing power of different currencies by eliminating the differences in price levels between countries.
Research and experimental development (R&D): R&D comprises creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge—including knowledge of humankind, culture, and society—and to devise new applications of available knowledge (OECD 2015).
R&D plant: Spending on R&D facilities and major equipment. Includes physical assets, such as land, structures, equipment, and intellectual property (e.g., software or applications).
Whole counting: This measure (also called full counting or integer counting) assigns one count to each region, country, or economy or institutional sector involved in coauthoring the article, irrespective of its proportionate involvement in authorship. Although fractional counting aims to assess the proportionate contributions of regions, countries, or economies or institutional sectors, whole counting aims to assess the participation of regions, countries, or economies or institutional sectors. One result of this difference is that the sum of articles from regions, countries, or economies or institutional sectors will exceed the total number of articles when whole counting is used. In the full-counting method, each publication is counted once for each entity listed in the address field.
Key to Acronyms and Abbreviations
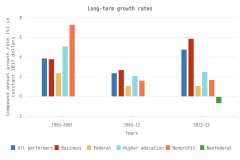
CAGR: compound annual growth rate
EU-27: European Union
FFRDC: federally funded research and development center
FY: fiscal year
GDP: gross domestic product
GERD: gross domestic expenditures on R&D
ISIC: International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities
KTI: knowledge- and technology-intensive
NAICS: North American Industry Classification System
NCSES: National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics
NSF: National Science Foundation
OECD: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
PPP: purchasing power parity
R&D: research and experimental development
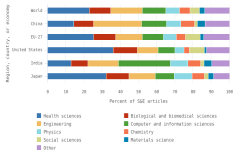
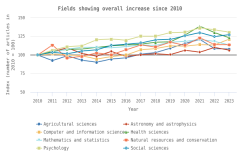
S&E: science and engineering
TOD: Taxonomy of Disciplines
 An official website of the United States government
An official website of the United States government