Annual Business Survey: 2020 (Data Year 2019)
General Notes
This report provides data from the 2020 Annual Business Survey (ABS) (data year 2019). The ABS is the primary source of data on research and development of for-profit, nonfarm businesses with one to nine employees operating in the 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia. The ABS also collects data on innovation, technology, intellectual property, and business owner characteristics of business of all sizes. The ABS is designed to incorporate new content each survey year based on topics of relevance. The 2020 ABS is the third year of the ABS. The survey is conducted annually by the Census Bureau for the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics within the National Science Foundation.
Data Tables
Survey aggregate estimates: 2019
Total R&D cost, by industry, employment size, sex, and race and ethnicity: 2019
R&D employees: 2019
R&D tax credit: 2019
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | View Table 23 | Download Table 23 XLSX | Download Table 23 PDF |
Product innovation: 2017–19
Business process innovation: 2017–19
Product or business process innovation: 2017–19
Innovation and R&D activity: 2017–19
Product or business process innovation: 2017–19
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 55 | View Table 55 | Download Table 55 XLSX | Download Table 55 PDF |
New-to-market product innovation: 2017–19
New-to-the-business product innovation: 2017–19
Product innovating companies and expectations: 2017–19
Product innovating companies and partners: 2017–19
Sales from most important innovation: 2017–19
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 74 | View Table 74 | Download Table 74 XLSX | Download Table 74 PDF |
Results of innovation activities: 2017–19
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 75 | View Table 75 | Download Table 75 XLSX | Download Table 75 PDF |
| 76 | View Table 76 | Download Table 76 XLSX | Download Table 76 PDF |
Innovation and government assistance: 2017–19
Company barriers and strategies: 2017–19
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 81 | View Table 81 | Download Table 81 XLSX | Download Table 81 PDF |
| 82 | View Table 82 | Download Table 82 XLSX | Download Table 82 PDF |
Digital technologies and innovation: 2017 – 19
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 83 | View Table 83 | Download Table 83 XLSX | Download Table 83 PDF |
| 84 | View Table 84 | Download Table 84 XLSX | Download Table 84 PDF |
Company methods of obtaining technology capabilities for innovation activities: 2017–19
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 85 | View Table 85 | Download Table 85 XLSX | Download Table 85 PDF |
| 86 | View Table 86 | Download Table 86 XLSX | Download Table 86 PDF |
Operating expenses: 2019
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 87 | View Table 87 | Download Table 87 XLSX | Download Table 87 PDF |
Activities conducted by unaffiliated companies: 2019
Companies with manufacturing activities in the United States: 2019
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 94 | View Table 94 | Download Table 94 XLSX | Download Table 94 PDF |
| 95 | View Table 95 | Download Table 95 XLSX | Download Table 95 PDF |
Companies with contracted out manufacturing: 2019
Companies that performed manufacturing tasks for unaffiliated companies or companies outside the United States: 2019
Companies with design or specification of goods for manufacturing activities completed by company 2019
| Table | View | Excel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 104 | View Table 104 | Download Table 104 XLSX | Download Table 104 PDF |
| 105 | View Table 105 | Download Table 105 XLSX | Download Table 105 PDF |
Technical Notes
Survey Overview (2020 Survey Cycle: Data Year 2019)
Purpose. The Annual Business Survey (ABS) provides information on selected economic and demographic characteristics for employer businesses and business owners by sex, ethnicity, race, and veteran status. Further, the survey measures research and development for microbusinesses, business topics such as innovation and technology, and other business characteristics. The ABS is conducted jointly by the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics (NCSES) within the National Science Foundation (NSF). The ABS replaces the quinquennial Survey of Business Owners (SBO) for employer businesses, the Annual Survey of Entrepreneurs (ASE), the Business R&D and Innovation for Microbusinesses Survey (BRDI-M), and the Innovation section of the Business R&D and Innovation Survey (BRDIS).
The ABS is designed to incorporate new content each survey year based on topics of relevance. For the 2020 ABS, content includes innovation, R&D, and domestic and foreign transactions. The ABS also collects various data regarding business owners, such as sex, ethnicity, race, veteran status, and other business characteristics. R&D data are collected on the ABS for businesses with a total employment range between 1 employee and 9 employees based on the number of employees the respondent indicates during the survey.
Data collection authority. Title 13, U.S. Code, Sections 8(b), 131, and 182; Title 42, U.S. Code, Sections 1861–76 (National Science Foundation Act of 1950, as amended); and Section 505 within the America COMPETES Reauthorization Act of 2010, authorize this collection. Sections 224 and 225 of Title 13 require mandatory response. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) No. 0607-1004.
Survey sponsor. NCSES within NSF.
Survey collection and tabulation agent. The survey is conducted annually by the U.S. Census Bureau in accordance with an interagency agreement with NCSES within NSF.
Key Survey Information
Frequency. Annual.
Initial survey year. 2017; for innovation, the reference period was 2015–17.
Reference period. 2019; for innovation, the reference period is 2017–19.
Response unit. Firm.
Sample or census. Sample.
Population size. 4.9 million employer firms; approximately 513,000 firms with 1–9 employees and in North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) industries 31–33 (manufacturing), 42 (wholesale trade), 51 (information), 5413 (architectural, engineering, and related services), 5415 (computer systems design and related services), or 5417 (scientific research and development services) were in scope for the R&D module.
Sample size. 300,000 employer businesses.
Survey Design
Target population. The target population consists of all companies that allocated most of their annual domestic payroll to for-profit entities and had at least one establishment that had paid employees based on the company's Internal Revenue Service Form 941 that covers 12 March 2020, was classified in an in-scope NAICS industry, was physically located in the United States, and was in business at the end of calendar year 2020.
Sampling frame. The sampling universe was constructed from the final 2018 Business Register. The Business Register is the Census Bureau’s comprehensive database of U.S. businesses. Business Register data are compiled from a combination of business tax returns, data collected from the economic census, and data from other Census Bureau surveys. The Business Register includes sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations reporting business activity to the IRS on any one of the following IRS tax forms: 1040 (Schedule C), “Profit or Loss from Business” (Sole Proprietorship); 1065, “U.S. Return of Partnership Income”; 941, “Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return”; 944, “Employer’s Annual Federal Tax Return”; or any one of the 1120 corporate tax forms.
The Business Register contains establishments that are out of scope for the ABS sample. These establishments are removed from the sampling universe. They include the following:
- Establishments engaged in the following NAICS industries:
- 110000, 111, or 112 - Agriculture production
- 482 - Railroads
- 491 - U.S. Postal Service
- 521 - Monetary authorities – central bank
- 525 - Funds, trusts, and other financial vehicles
- 813 - Religious, grantmaking, civic, professional, and similar organizations
- 814 - Private households
- 92 - Public administration
- Unclassified with legal form of organization as tax-exempt or unknown
- Establishments located in American Samoa, Northern Mariana Islands, Guam, Puerto Rico, or the U.S. Virgin Islands
- Establishments belonging to foreign entities
- Government establishments
- Establishments with zero payroll and zero employment
- Establishments identified as out of business during prior year data review
- Single-unit establishments modeled as likely to be out of business using administrative data from the most recent monthly business register data sets
Information on industry classification, receipts, payroll, and employment was extracted from the Business Register during the frame construction.
The sample is also designed to estimate demographic characteristics of the business owners. To efficiently sample for demographic characteristics, a variety of sources of information is used to estimate the likelihood that a business is a woman- or minority-owned business. Administrative sources include the Decennial Census, the American Community Survey (ACS), and the Numident file, which is the Social Security Administration’s (SSA) comprehensive database of information from Social Security applications. Individual business owners are identified through IRS K-1 filings for partnerships and corporations and from the Business Register for sole proprietorships. The owners are matched to the 2000 and 2010 Decennial Censuses to get race, sex, and ethnicity data; to the 2000–17 ACS; and to the Numident file (in that order) through a Protected Identification Key. Country of birth is also identified through the linkages to the ACS or Numident data. Each firm is then placed in one of the following nine frames for sampling: American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, Black or African American, Hispanic, non-Hispanic White men, Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander, other, publicly owned, and women. Businesses are assigned to one and only one frame, with priority given to the less common frames.
Sample design. The ABS frame is stratified by geographic area defined by state, strata, and industry and is systematically sampled within each stratum. A standard type of estimation for stratified systematic sampling is used. Large companies were selected with certainty based on volume of sales, payroll, or number of paid employees. Specifically for the 2020 ABS, firms were selected with certainty based on the following criteria:
- firms with more than 500 employees,
- firms that had more than $1 million in R&D expenses reported in prior year ABS, or
- firms larger than stratum-specific payroll and receipt cutoffs.
The certainty cutoffs vary by sampling stratum, and each stratum is sampled at varying rates, depending on the number and size of firms in a particular stratum.
The remaining frame is subjected to stratified systematic random sampling. Sampling rates vary by strata and are determined by the following calculations. Note that a systematic sample uses take rate to sample where the sampling rate is 1/take rate. Additional sample design details are available in the 2020 Annual Business Survey Methodology Report.
The ABS sample consisted of 300,000 businesses. There were 43,000 selected with certainty. The certainty portion of the sample consisted of
- 17,000 with employment ≥ 500,
- 2,100 with R&D expenses greater than $1 million in previous cycles of the ABS,
- 16,000 with payroll above the stratum cutoff, and
- 7,900 with receipts above the stratum cutoff. (Note that payroll cutoffs are applied first so cases above both cutoffs appear in payroll count.)
The remaining 253,000 noncertainty cases were selected using the systematic stratified random sample selection. The maximum sample weight was 40.
Data Collection and Processing Methods
Data collection. Prior to mailing the survey, certain businesses selected were determined to be out of scope and were not contacted. The survey was mailed to 300,000 employer businesses in July 2020. Businesses were sent a letter informing them of their requirement to report. The letter also provided instructions on how to access the survey and submit online. There were three mail follow-ups conducted to increase response. The third mail follow-up included a paper questionnaire for select nonrespondents. Additionally, the Census Bureau conducted e-mail follow-ups to respondents who entered the electronic system but did not submit the questionnaire. The collection period closed in January 2021.
Mode. The 2020 ABS was collected using both a paper form and the electronic instrument.
Check-in rate. The check-in rate is defined as the unweighted number of surveys that were submitted online by in-scope companies, divided by the unweighted total number of all in-scope companies in the sample. Response to individual questions did not factor into this metric. At the close of the collection period in January 2021, there were 201,000 responses submitted. Of those, 194,000 reported online (64.67% of the sample), and 7,000 reported using the paper questionnaire (0.023% of the sample).
There were an additional 3,600 businesses that contacted the Census Bureau to indicate that the business was no longer in operation or had been sold for the reference year via the call center.
Businesses selected to report R&D represented 36.3% of those mailed. Of the businesses mailed and selected to report R&D, 73,500 businesses (or 67.4%) submitted responses.
Unit response rate (URR). The URR is the unweighted number of responding companies for the survey. For the ABS, response is defined as a company providing the number of owners, number of paid owners, and number of employees or a company responding that it ceased operations prior to 2019.
For the ABS, the URR was 71.7%. The URR for businesses eligible to report the R&D module was 75.0%.
Item response rates (IRR). The 2020 ABS collected data on approximately 650 variables, and the distribution of values reported by sample companies is highly skewed. Thus, rather than report unweighted item response rates, total quantity response rates are calculated, which are based on weighted data. The survey skip patterns vary for respondents; therefore, it can be impossible to know an exact denominator for item response calculations.
Total quantity response rate (TQRR). For a given published estimate other than count or ratio estimates, TQRR is the percentage of the weighted estimate based on data that were reported by units in the sample or on data that were obtained from other sources and were determined to be equivalent in quality to reported data and weighted only by sampling but not nonresponse weights. The TQRR for total sales in the United States in 2019 was 67.9%.
Total quantity nonresponse rate (TQNR). For a given published estimate, TQNR, defined as 100% minus TQRR, is calculated for each tabulation cell from the ABS, except for cells that contain count or ratio estimates. TQNR measures the combined effect of the procedures used to handle unit and item nonresponse on the weighted ABS estimate. Detailed imputation rates are available on request.
Data editing. Prior to tabulating the data, response data were reviewed and edited to correct reporting errors. R&D data were tabulated for records reporting $50,000 or more in R&D expenditures.
Additionally, R&D data were only tabbed for records classified in the following NAICS industries:
- 31–33 - Manufacturing
- 42 - Wholesale trade
- 51 - Information
- 5413 - Architectural, engineering, and related services
- 5415 - Computer systems design and related services
- 5417 - Scientific research and development services
Survey analysts reviewed the R&D reported by the survey respondents. Research was done by evaluating the reported business descriptions, reported R&D-to-sales ratio, and company website information. The majority of corrections involved false-positive reports or data reported using incorrect units (such as whole dollars instead of thousands of dollars). For NAICS industries 5415 and 5417, it is difficult to differentiate R&D from other technical work based solely on company website information. Due to this difficulty and the large number of companies sampled in these industries, it was not feasible to review each case individually; thus, relatively few corrections were made for false-positive reports. Unlike years past, we were able to review all cases in these industries that had greater than $50,000 in R&D expenses.
Additional data errors were detected and corrected through mass corrections and an automated data edit system designed to review the data for reasonableness and consistency. The editing process interactively performed corrections by using standard procedures to fix detectable errors. Quality control techniques were used to verify that operating procedures were carried out as specified.
Techniques for handling unit nonresponse. Weighted estimates produced from the ABS include adjustments to account for companies that did not respond to the survey (unit nonresponse).
Unit nonresponse. Unit nonresponse is handled by adjusting weighted reported data as follows. Each company’s sampling weight is multiplied by a nonresponse adjustment factor. To calculate the adjustment factors, each company in the sample that is eligible for tabulation is assigned to one (and only one) adjustment cell. The adjustment cells are based on employment size and NAICS sector. For employment size, there are five categories: 1–4 employees, 5–9 employees, 10–49 employees, 50–249 employees, and 250 or more employees. For a given adjustment cell, the nonresponse adjustment factor is the ratio of the sum of the sampling weights for all companies in the cell to the sum of the sampling weights for all companies in the cell with reported data. For the nonresponse adjustment, a business is considered a respondent if it responded to either the R&D module, innovation module, or technology module of the survey.
Weighting. The survey data are weighted for sampling as designed for the ABS. The weights were adjusted for complete nonresponse using a nonresponse adjustment factor that, when multiplied by the original sampling weights, ensures that respondent firms in each cell are representative of both respondents and nonrespondents. Firms were grouped into nonresponse adjustment cells by sector and employment size, and the nonresponse adjustment factor for adjustment cell h was calculated as:
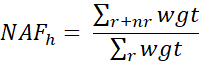
where
r is the partial and complete respondents (RESP in (“CR,” “PR”)),
nr is the complete nonrespondents (RESP = “NR”),
wgt is the TAB_WGT value,
h is the adjustment cell (SECTOR × EMPSIZE_COLLAPSE), and
NAFh is the nonresponse adjust factor for cell h.
Tabulation. Though as many firms as possible were identified as out of scope during sampling, additional out-of-scope firms were identified with either response or updated administrative data not available at the time of sampling. These 34,500 firms were removed for tabulations and include
- firms reporting zero employment,
- firms that responded as having gone out of business before 2019,
- nonprofit organizations,
- firms that responded as being owned by a domestic parent company, and
- firms with unclassified NAICS industry.
Industry classification. The industry classifications of firms are based on the 2017 NAICS (https://www.census.gov/naics/). Firms with more than one domestic establishment are assigned a single industry classification using a hierarchal system based on the largest payroll sector, largest payroll 3-digit NAICS (within the largest sector), largest payroll 4-digit NAICS (within the largest 3-digit), and largest payroll 6-digit NAICS (within the largest 4-digit). For tabulation, industry classification was based on administrative data for 2017.
Geography. Firms with establishments operating in more than one state are tabulated as unclassified and counted only once in state and national totals.
Variance estimation. The ABS uses the delete-a-group jackknife variance estimator. Note that certainty cases do not contribute to the sampling variance. The delete-a-group jackknife variance estimator requires that every sampling stratum contains at least two sampled firms. Sampling strata that do not meet this requirement are collapsed as needed to create a new set of variance estimation strata that satisfies this requirement.
Detailed relative standard errors may be found in the accompanying tables denoted as _err.
Survey Quality Measures
The estimates produced from the ABS are subject to both sampling and nonsampling errors.
Sampling error. The sampling error is described above in the variance estimation section.
Coverage error. Coverage error occurs when the frame fails to completely enumerate the population of interest. There can be both undercoverage error, where units are not included in the frame, and overcoverage error, where units included in the frame are actually out of scope for the population of interest. The ABS uses the prior year Business Register to construct the frame, so any changes in businesses that would change the inclusion or exclusion of the business to the survey scope could be sources of coverage error. Prior to tabulation, survey units’ information is updated with the most recent available Business Register data to mitigate this source of error.
Nonsampling error. All surveys and censuses have nonsampling errors. Nonsampling errors are attributable to various sources, such as the inability to obtain information for all cases in the universe, imputation for missing data, data errors and biases, mistakes in recording or keying data, errors in collection or processing, and coverage problems.
While explicit measures of the effects of these nonsampling errors are not available, adjustments are made to the published relative standard errors to account for errors associated with imputation of missing data. It is believed that most of the important operational and data errors were detected and corrected through an automated data edit designed to review the data for reasonableness and consistency. Quality control techniques were used to verify that operating procedures were carried out as specified.
Measurement error. Expected sources of measurement error include differences in respondent interpretations of the definitions of R&D activities and differences in how companies count and report numbers of employees in various categories, including whether they work on R&D full time or part time. Little public information exists for most of the small businesses surveyed by the ABS, so it is difficult to determine whether companies are reporting R&D that satisfies the survey's definitions, particularly where the development of software and internet applications are concerned. Although quantitative metrics of measurement error are not available, there are ongoing efforts to minimize measurement error, including questionnaire pretesting, improvement of questionnaire wording and format, inclusion of more cues and examples in the questionnaire instructions, in-person and telephone interviews and consultations with respondents, and post-survey evaluations. The most common source of measurement error was reporting in different units (e.g., reporting whole dollars rather than thousands of dollars).
Data Comparability
Some estimates from the 2020 ABS may not be directly comparable to similar estimates from prior ABS results due to changes in survey methodology. Sources of possible incomparability include changes to questionnaire wording and instructions, changes to data editing and tabulation, and changes to imputation and nonresponse adjustments.
Changes to questionnaire. The survey section that collected information on R&D from businesses (section D) had nearly identical question wording and instructions for both the ABS 2020 and the ABS 2018 questionnaires. The 2020 ABS collected additional detail from businesses on the location of R&D performance and explicitly highlighted the concept of “domestic R&D performance.” For the 2020 ABS detailed questions about R&D expenditures (types of costs, funding sources, and R&D categories) were tied to domestic R&D performance (a subset of total R&D costs), whereas the 2018 ABS asked similar questions tied to total R&D costs.
The following are survey changes in the questionnaire from ABS 2019 to ABS 2020; question number references are in reference to the ABS 2020:
- A.14 Franchise question is new
- A.15 Working from home question is new
- A.16 Percentage of employees working from home question is new
- A.17 Factors affecting working from home question is new
- Questions on product innovation, C.1 and C.2 (goods and services) are modified
- C.5 Expectations question is new
- C.7 Goods or services cooperation partners question is new
- C.8 Goods or services cooperation partners location question is new
- C.9 Most important innovation question is new
- C.10 Most important innovation and sales question is new
- C.13 Goods, services, or business process activities question has additional text in the question
- C.14 Results of innovation activities question is new
- C.15 Activity costs question now asks for the total only—there is no longer a breakdown of the kinds of costs
- C.17 Government support question is new
- C.18 Barriers of innovation question is new
- C.19 Business strategies question is new
- C.20 Use of digital technologies question is new
- C.21 Capabilities for using digital technologies question is new
- C.22 Technology capabilities question is new
- D.7 The option for U.S. federal government now includes a question about which agency provides the largest share
- Technology and intellectual property (section E in ABS 2019) is not included in the ABS 2020
- Section E: Domestic and foreign transaction is new
Changes to data editing and tabulation. For data collected in the R&D section of the ABS, every response with $50,000 or more in R&D costs was reviewed for reasonableness in 2019. For the 2018 ABS, all positive R&D cases were reviewed in industries with high rates of false-positive reports. Outside of the review for potential false-positive R&D cases, the editing of R&D data was performed similarly in 2017 and 2018. There have been no major changes to the edits from year to year.
Data collected in the innovation section of the ABS were edited similarly in 2017 and 2018, but the estimates for product innovation were tabulated differently. For 2017, a business must have responded positively to both the product innovation question and the subsequent business product innovation question (new to market or new to business) to be considered a product innovator. For 2018 and 2019, only a positive response to the question regarding new or improved goods or services was required to be tabulated as a product innovator.
Changes in imputation methods. In 2019, a change was made in how item nonresponse is treated in ABS. Item nonresponse occurs when a company responds to the survey but leaves some items blank. In 2018, item nonresponse was treated using a combination of mode and donor imputation. For 2019 and future years (including 2020), no imputation was performed to treat item nonresponse, and missing items were included as no’s or zeros in the estimates. For the majority of the estimates (91%), this change in methods did not yield a change in the estimates. For an additional 9% of estimates, there was a difference in the estimate; the difference, however, was not statistically significant.
Changes in collection methods. During the 2020 ABS collection period, a split mailing was conducted to assess the impact of using a U.S. Postal Service (USPS) Certified Mail letter versus USPS Priority Mail letter. Additionally, the paper form mailing was moved up to the second follow-up as compared to the third follow-up for the 2019 ABS due to the COVID-19 pandemic. For the 2020 ABS, the third follow-up was conducted as a Census Certified Mail letter.
Definitions
- Affiliated (company or business). An entity that is owned 10% or more (based on voting interest or an equivalent interest) directly or indirectly by your company.
- Business processes. Business process includes the following: (1) methods for producing goods or providing services, (2) distribution and logistics, (3) marketing and sales, (4) information and communication systems, (5) administration and management activities, and (6) product and business process development (including activities to identify, develop, or adapt products or a firm’s processes).
- Core production activity. This term refers to your primary business activities. For manufacturing companies, core production typically involves production of physical goods. For service companies and other companies, core production refers to the main services or activities provided by your business, such as information and communications technology services, marketing services, etc.
- Domestic or U.S.-located. Refers to a location in any of the U.S. 50 states and the District of Columbia.
- Employment. Paid employment consists of full- and part-time employees, including salaried officers and executives of corporations who were on the payroll in the pay period including March 12. Included are employees on sick leave, holidays, and vacations; not included are proprietors and partners of unincorporated businesses.
- Ethnicity. Based on OMB’s guidance, there are two minimum categories for ethnicity: Hispanic or Latino and Not Hispanic or Latino. OMB considers race and Hispanic origin to be two separate and distinct concepts. Hispanics and Latinos may be of any race.
- Exported goods. Value of goods, including the value of equipment, supplies, materials, etc. This should equal the amounts reported in the Automated Export System’s Electronic Export Information filed with U.S. Customs and Border Protection plus the cost of transporting the goods to customers located in foreign destinations (i.e., outside the United States).
- Exported services. An exported service is a service-related product (i.e., services performed, including digital service, license agreement) that is sold or transferred to, or performed for, customers (individual, government, business establishment, etc.) located in foreign destinations (i.e., outside the United States).
- Firm. A business organization or entity consisting of one or more domestic establishment locations under common ownership or control.
- Foreign affiliate. A foreign affiliate is an entity located outside the United States that is owned at least 10% (based on voting interest or an equivalent interest) directly or indirectly by the U.S. reporter.
- Foreign parent (of a U.S.-located business). The first entity outside the United States in an affiliate’s ownership chain that has a direct or indirect investment interest of more than 50% of the affiliate’s voting securities.
- Goods. Usually a tangible object (such as a smartphone, furniture, or packaged software) but also includes digital goods (such as downloadable software, music and film). Exclude the simple resale of new goods and changes of a solely aesthetic nature.
- Imported goods. The value of goods purchased from customers located in foreign destinations (i.e., outside the United States) as indicated in import declarations filed with the U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
- Imported services. An imported service is a service-related product (i.e., service performed, including digital service, license agreement) that is purchased from customers located in foreign destinations (i.e., outside the United States).
- Innovation. A business innovation is a new or improved product or business process (or combination thereof) that differs significantly from the firm’s previous products or business processes and that has been introduced on the market or brought into use by the firm.
- Intellectual property. Includes patents, processes, and trade secrets; books and music; trademarks; recorded performances and events, such as radio and television programs and motion pictures; broadcast and recorded live performances and events and their content; general use computer software; franchise fees; and other (e.g., digital media).
- Noise infusion. A method of disclosure avoidance in which values are perturbed prior to tabulation by applying a random noise multiplier to the magnitude data, such as the sales and receipts for all firms. Disclosure protection is accomplished in a manner that causes the vast majority of cell values to be perturbed by, at most, a few percentage points.
- North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). NAICS is the standard used by federal statistical agencies in classifying business establishments for the purpose of collecting, analyzing, and publishing statistical data related to the U.S. business economy. This system is used by the United States, Canada, and Mexico.
- Race. The data on race were derived from answers to the race question. Race data are collected in accordance with the guidelines provided by OMB, and these data are based on self-identification. The racial categories included in the questionnaire generally reflect a social definition of race recognized in this country and not an attempt to define race biologically, anthropologically, or genetically. In addition, it is recognized that the categories of the race question include race and national origin or sociocultural groups. OMB requires that race data be collected for a minimum of five groups: White, Black or African American, American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander. Respondents may report more than one race.
- Receipts. Includes the total sales, shipments, receipts, revenue, or grants for domestic operations, excluding foreign subsidiaries.
- Research and development (R&D). R&D is planned, creative work aimed at discovering new knowledge or devising new applications of available knowledge. This includes (1) activities aimed at acquiring new knowledge or understanding without specific immediate commercial applications or uses (basic research); (2) activities aimed at solving a specific problem or meeting a specific commercial objective (applied research); and (3) systematic use of research and practical experience and resulting in additional knowledge, which is directed to producing new or improved goods, services, or processes (development). R&D includes both direct costs, such as salaries of researchers, and administrative and overhead costs clearly associated with the company’s R&D. However, R&D does not include expenditures for routine product testing, quality control, and technical services unless they are an integral part of an R&D project. R&D also does not include market research; efficiency surveys or management studies; literary, artistic, or historical projects, such as films, music, or books and other publications; and prospecting or exploration for natural resources.
- Basic research. Activities aimed at acquiring new knowledge or understanding without specific immediate commercial applications or uses.
- Applied research. Activities aimed at solving a specific problem or meeting a specific commercial objective.
- Development. Systematic work, drawing on research and practical experience and resulting in additional knowledge, which is directed to producing new products or processes or to improving existing products or processes.
- R&D activity in software includes:
- Software development or improvement activities that expand scientific or technological knowledge
- Construction of new theories and algorithms in the field of computer science
- R&D activity in software excludes:
- software development that does not depend on a scientific or technological advance, such as
- supporting or adapting existing systems,
- adding functionality to existing application programs,
- routine debugging of existing systems and software, and
- creation of new software based on known methods and applications;
- conversion or translation of existing software and software languages; and
- adaptation of a product to a specific client, unless knowledge that significantly improved the base program was added in that process.
- Services. Intangible activities, such as retailing, insurance, educational courses, air travel, consulting, etc.; also includes digital services. (Exclude the simple resale of new services.)
- Sex. For the purposes of the ABS, sex refers to a person’s biological sex. The sex question wording very specifically intends to capture a person’s biological sex and not gender.
- Unaffiliated (company or business). Entity that is owned less than 10%, directly or indirectly, by your company (i.e., independent contractors and suppliers).
- Worldwide sales. Worldwide and domestic sales and operating revenues, including grants.
Technical Tables
Acknowledgments and Suggested Citation
Acknowledgments
Audrey E. Kindlon of the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics (NCSES) developed and coordinated this report under the guidance of John Jankowski, NCSES Program Director, and under the leadership of Emilda B. Rivers, NCSES Director; Vipin Arora, NCSES Deputy Director; and Matt Williams, Acting NCSES Chief Statistician. In partnership with NCSES, the Census Bureau conducted the survey and prepared the tables. NCSES staff members who made significant contributions include Gary Anderson, Jock Black, Jennifer Beck, Rebecca Morrison, and Timothy Wojan.
The Census Bureau, under National Science Foundation interagency agreement number NCSE-1748418, collected, processed, evaluated, and tabulated the data for this report. The Annual Business Survey is conducted within the Economic Directorate of the Census Bureau under the direction of Nick Orsini, Associate Director for Economic Programs, and Stephanie Studds, Assistant Director for Economic Programs.
The data were prepared in the Economic Reimbursable Surveys Division under the direction of Kevin Deardorff, Division Chief, and Aneta Erdie, Assistant Division Chief. This work was performed under the supervision of Patrice Hall, assisted by John Clark, Lakitquana Leal, and Gail White, with staff assistance from Concepcion Arenas Alvarez, Ahmad Bakhshi, Elaine Emanuel, Mary Frauenfelder, Aaron Finkle, Samantha Hernandez, James Jarzabkowski, Jessica Welch, and Tesfay Weldu. Additional support, including table creation and subject matter expertise was provided by Brandon Shackelford.
Mathematical and statistical techniques were provided by the Economic Statistical Methods Division under the direction of James Hunt, Assistant Division Chief. This work was performed under the supervision of Roberta Kurec, assisted by Sandra Peterson, with staff support from Taylor Beebe, Alexandra Abzun Cadenas, Charles Champion, and Daniel Cordes.
Data collection procedures and operations were provided by the Economic Management Division under the direction of Lisa Donaldson, Division Chief, and Michelle Karlsson, Assistant Division Chief. The staff of the National Processing Center performed mailout preparation, respondent assistance, and correspondence processing. Project management support was provided by Laura Hardesty.
Development and coordination of the computer processing system was provided by the Economic Application Division under the direction of Sumit Khaneja, Division Chief and Olajumoke Oyewole, Assistant Division Chief. This work was performed by Marilyn Balogh, Michael Feldman, David Gonzalez, Chakravarthy Sharad, and Joseph Talbot.
Publication processing support was provided by Devi Mishra, Christine Hamel, and Tanya Gore (NCSES).
Suggested Citation
National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics (NCSES). 2022. Annual Business Survey: 2020 (Data Year 2019). NSF 22-344. Alexandria, VA: National Science Foundation. Available at https://ncses.nsf.gov/pubs/nsf22344/.
Contact Us
NCSES
National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics
Directorate for Social, Behavioral and Economic Sciences
National Science Foundation
2415 Eisenhower Avenue, Suite W14200
Alexandria, VA 22314
Tel: (703) 292-8780
FIRS: (800) 877-8339
TDD: (800) 281-8749
E-mail: ncsesweb@nsf.gov
 An official website of the United States government
An official website of the United States government


