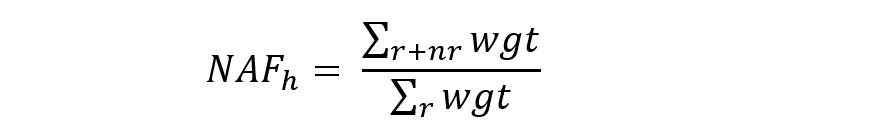Data collection. Prior to mailing the survey, certain businesses selected were determined to be out of scope and were not contacted. The survey was mailed to 300,000 employer companies in July 2021. Businesses were sent a letter informing them of their requirement to report. The letter also provided instructions on how to access the survey and submit online. There were three mail follow-ups conducted to increase response. Additionally, the Census Bureau conducted e-mail follow-ups to respondents who entered the electronic system but did not submit the questionnaire. The collection period closed in January 2022.
Mode. The 2021 ABS was collected using the electronic instrument.
Check-in rate. The check-in rate is defined as the unweighted number of surveys that were submitted online by in-scope companies, divided by the unweighted total number of all in-scope companies in the sample. Response to individual questions did not factor into this metric. At the close of the collection period in January 2022, there were 190,000 responses submitted (63% of the sample).
There were an additional 1,800 businesses that contacted the Census Bureau via the call center to indicate that the company was no longer in operation or had been sold for the reference year.
Companies selected to report R&D represented 37.2% of those mailed. Of the companies mailed and selected to report R&D, 76,000 companies (or 68%) submitted responses.
Unit response rate (URR). The URR is the unweighted number of responding companies for the survey. For the ABS, response is defined as a company providing the number of owners, number of paid owners, and number of employees; or a company responding that it ceased operations prior to 2020.
For the ABS, the URR was 68.8%. The URR for businesses eligible to report the R&D module was 73.1%
Item response rates (IRR). The 2021 ABS collected data on approximately 650 variables, and the distribution of values reported by sample companies is highly skewed. Thus, rather than report unweighted item response rates, total quantity response rates are calculated, which are based on weighted data. The survey skip patterns vary for respondents; therefore, it is not possible to know an exact denominator for item response calculations.
Total quantity response rate (TQRR). For a given published estimate other than count or ratio estimates, TQRR is the percentage of the weighted estimate based on data that were reported by units in the sample or on data that were obtained from other sources and were determined to be equivalent in quality to reported data and weighted only by sampling but not nonresponse weights. The TQRR for total sales in the United States in 2020 was 72.9%.
Total quantity nonresponse rate (TQNR). For a given published estimate, TQNR, defined as 100% minus TQRR, is calculated for each tabulation cell from the ABS, except for cells that contain count or ratio estimates. TQNR measures the combined effect of the procedures used to handle unit and item nonresponse on the weighted ABS estimate. Detailed imputation rates are available on request from the survey manager.
Data editing. Prior to tabulating the data, response data were reviewed and edited to correct reporting errors. R&D data were tabulated for records reporting $50,000 or more in R&D expenditures.
Additionally, R&D data were only tabbed for records classified in the following NAICS industries:
- 31–33 - Manufacturing
- 42 - Wholesale trade
- 51 - Information
- 5413 - Architectural, engineering, and related services
- 5415 - Computer systems design and related services
- 5417 - Scientific research and development services
Survey analysts reviewed the R&D reported by the survey respondents. Research was done by evaluating the reported business descriptions, reported R&D-to-sales ratio, and company website information. The majority of corrections involved false-positive reports or data reported using incorrect units (such as whole dollars instead of thousands of dollars). For NAICS industries 5415 and 5417, it is difficult to differentiate R&D from other technical work based solely on company website information. Due to this difficulty and the large number of companies sampled in these industries, it was not feasible to review each case individually; thus, relatively few corrections were made for false-positive reports. Unlike years past, we were able to review all cases in these industries that had greater than $50,000 in R&D expenses.
Additional data errors were detected and corrected through mass corrections and an automated data edit system designed to review the data for reasonableness and consistency. The editing process interactively performed corrections by using standard procedures to fix detectable errors. Quality control techniques were used to verify that operating procedures were carried out as specified.
Unit nonresponse. Unit nonresponse is handled by adjusting weighted reported data as follows. Each company’s sampling weight is multiplied by a nonresponse adjustment factor. To calculate the adjustment factors, each company in the sample that is eligible for tabulation is assigned to one (and only one) adjustment cell. The adjustment cells are based on employment size and NAICS sector. For employment size, there are five categories: 1–4 employees, 5–9 employees, 10–49 employees, 50–249 employees, and 250 or more employees. For a given adjustment cell, the nonresponse adjustment factor is the ratio of the sum of the sampling weights for all companies in the cell to the sum of the sampling weights for all companies in the cell with reported data. The nonresponse adjustment factor for adjustment cell h was calculated as:
The nonresponse adjustment factor for cell h is equal to the sum of weights for the respondents and nonrespondents in the cell divided by the sum of the weights for the respondents in the cell.
where
|
r |
is the partial and complete respondents (RESP in (“CR,” “PR”)), |
|
nr |
is the complete nonrespondents (RESP = “NR”), |
|
wgt |
is the TAB_WGT value, |
|
h |
is the adjustment cell (SECTOR × EMPSIZE_COLLAPSE), and |
|
NAFh |
is the nonresponse adjust factor for cell h. |
For the nonresponse adjustment, a company is considered a respondent if it responded to either the R&D module, innovation module, or technology module of the survey.
Tabulation. Though as many firms as possible were identified as out of scope during sampling, additional out-of-scope firms were identified with either response or updated administrative data not available at the time of sampling. These 21,000 firms were removed for tabulations and include
- firms reporting zero employment,
- firms that responded as having gone out of business before 2020,
- nonprofit organizations,
- firms that responded as being owned by a domestic parent company, and
- firms with unclassified NAICS industry.
Industry classification. The industry classifications of firms are based on the 2017 NAICS (https://www.census.gov/naics/). Firms with more than one domestic establishment are assigned a single industry classification using a hierarchal system based on the largest payroll sector, largest payroll 3-digit NAICS (within the largest sector), largest payroll 4-digit NAICS (within the largest 3-digit), and largest payroll 6-digit NAICS (within the largest 4-digit). For tabulation, industry classification was based on administrative data for 2017.
Geography. Firms with establishments operating in more than one state are tabulated as unclassified geography and counted only once in state and national totals.
Variance estimation. The ABS uses the delete-a-group jackknife variance estimator. Note that certainty cases do not contribute to the sampling variance. The delete-a-group jackknife variance estimator requires that every sampling stratum contains at least two sampled firms. Sampling strata that do not meet this requirement are collapsed as needed to create a new set of variance estimation strata that satisfies this requirement.
Detailed relative standard errors are available on request from the survey manager.
 An official website of the United States government
An official website of the United States government